HealthPub Publishes Comprehensive FODMAP Statistics Report
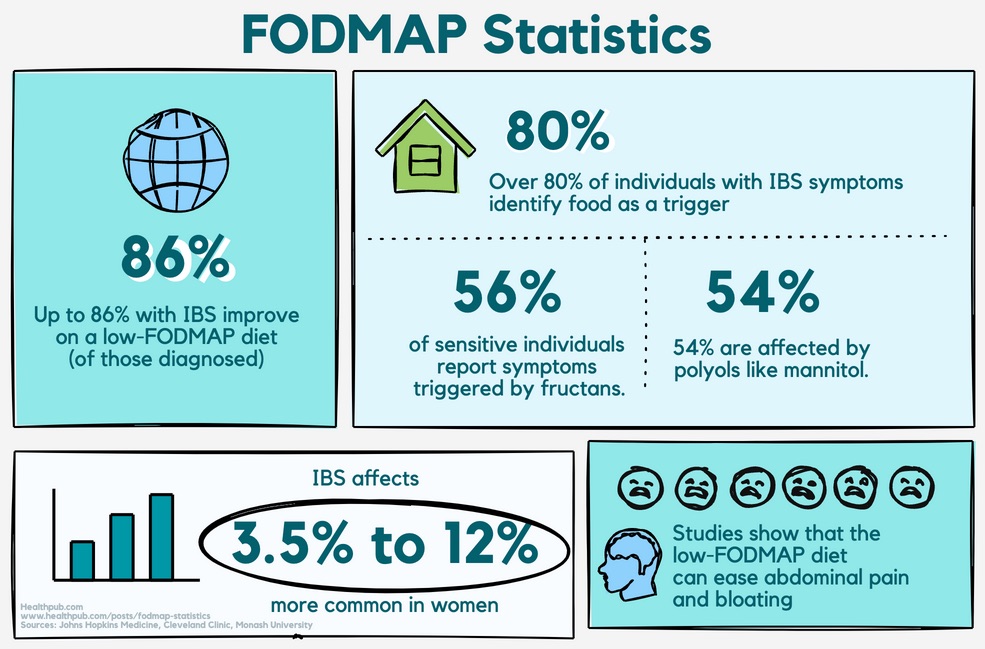
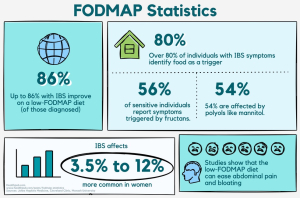
Research highlights that up to 86% of IBS sufferers experience significant symptom relief by following a low-FODMAP diet, emphasizing its effectiveness in managing bloating, abdominal pain, and irregular bowel movements.
New York, NY, November 23, 2024 --(PR.com)-- FODMAPs, short for Fermentable Oligosaccharides, Disaccharides, Monosaccharides, and Polyols, are a group of poorly absorbed carbohydrates known to trigger digestive discomfort in sensitive individuals.
For individuals with conditions like Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), managing FODMAP sensitivities is crucial for improving quality of life. This report explores key statistics and insights about FODMAPs and their impact on health.
Studies indicate that up to 86% of individuals with IBS experience symptom relief when following a low-FODMAP diet. This statistic highlights the diet's effectiveness in addressing symptoms such as bloating, abdominal pain, and irregular bowel movements.
Notably, the prevalence of IBS ranges from 3.8% to 12% in the general population, with women being more commonly affected. For more in-depth data, HealthPub’s FODMAP Statistics resource provides key facts and additional insights into food sensitivities.
Among individuals with sensitivities, 56% report that fructans - found in foods like garlic and onions - are major triggers, while 54% identify polyols such as mannitol. These figures underscore the importance of identifying and avoiding specific high-FODMAP foods to manage symptoms effectively.
Beyond statistics, the low-FODMAP diet offers practical benefits. Research suggests it can reduce stool frequency, improve stool consistency, and significantly minimize discomfort for IBS sufferers. By identifying specific FODMAP triggers, individuals can create personalized dietary plans that alleviate symptoms without compromising nutritional needs.
Some of the most common high-FODMAP foods include:
Garlic and onions
Wheat and rye products
Certain fruits such as apples and cherries
Dairy products containing lactose
Identifying these foods is essential for managing digestive health. Consulting reliable low-FODMAP resources can assist in developing a tailored dietary approach.
HealthPub remains committed to providing resources that support individuals in better understanding their health. Detailed statistics, dietary tips, and expert advice are available to help those with food sensitivities be more informed.
For more insights and detailed findings, visit the FODMAP Statistics page on the HealthPub website. By staying informed and collaborating with healthcare professionals, individuals can take control of their digestive health and lead a more comfortable, symptom-free life.
For individuals with conditions like Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS), managing FODMAP sensitivities is crucial for improving quality of life. This report explores key statistics and insights about FODMAPs and their impact on health.
Studies indicate that up to 86% of individuals with IBS experience symptom relief when following a low-FODMAP diet. This statistic highlights the diet's effectiveness in addressing symptoms such as bloating, abdominal pain, and irregular bowel movements.
Notably, the prevalence of IBS ranges from 3.8% to 12% in the general population, with women being more commonly affected. For more in-depth data, HealthPub’s FODMAP Statistics resource provides key facts and additional insights into food sensitivities.
Among individuals with sensitivities, 56% report that fructans - found in foods like garlic and onions - are major triggers, while 54% identify polyols such as mannitol. These figures underscore the importance of identifying and avoiding specific high-FODMAP foods to manage symptoms effectively.
Beyond statistics, the low-FODMAP diet offers practical benefits. Research suggests it can reduce stool frequency, improve stool consistency, and significantly minimize discomfort for IBS sufferers. By identifying specific FODMAP triggers, individuals can create personalized dietary plans that alleviate symptoms without compromising nutritional needs.
Some of the most common high-FODMAP foods include:
Garlic and onions
Wheat and rye products
Certain fruits such as apples and cherries
Dairy products containing lactose
Identifying these foods is essential for managing digestive health. Consulting reliable low-FODMAP resources can assist in developing a tailored dietary approach.
HealthPub remains committed to providing resources that support individuals in better understanding their health. Detailed statistics, dietary tips, and expert advice are available to help those with food sensitivities be more informed.
For more insights and detailed findings, visit the FODMAP Statistics page on the HealthPub website. By staying informed and collaborating with healthcare professionals, individuals can take control of their digestive health and lead a more comfortable, symptom-free life.
Contact
Healthpub
Paul Michael
+1 609-316-6957
https://www.healthpub.com/
Paul Michael
+1 609-316-6957
https://www.healthpub.com/
Multimedia
Infograph of FODMAP Statistics
Infograph of FODMAP Statistics
Categories
